Primordial Patterns: Archetypes in the Universe
The concept of archetypes has captivated thinkers for centuries, suggesting that beneath the chaotic surfaces of life lies a deep, pervasive order. From the ancient philosophies to modern psychology and cosmology, archetypes are seen as immutable constellations of meaning, framing human experiences and universal phenomena.
Understanding Archetypes
Archetypes are often conceived as primordial patterns or universal symbols that manifest in the mythology, art, religions, and dreams of people, transcending cultural and temporal boundaries. Carl Jung, a pivotal figure in the exploration of this concept, described archetypes as innate, universal prototypes for ideas, experienced as recurring motifs throughout human history.
“He who looks outside, dreams; he who looks inside, awakes.” — Carl Jung
In this sense, archetypes are abstract metaphors residing in the collective unconscious, representing fundamental human motifs of experience and action. They appear in our minds as latent possibilities rather than fully realized concepts, shaping the constitutive elements of our stories, dreams, and perceptions.
Archetypes in Mythology and Culture
The role of archetypes in mythology serves as an essential tool for understanding the collective psyche. Joseph Campbell famously worked with Jungian archetypes in his seminal work, The Hero with a Thousand Faces, where he outlines the Hero’s Journey, a common narrative template found across diverse mythologies.
- The Hero: Embarks on an adventure, faces trials, and transforms at the journey’s end.
- The Mentor: Provides guidance, insight, or aid to the Hero.
- The Shadow: Represents the adversary, a crucial element that advocates overcoming adversity.
These archetypal figures and narratives echo through contemporary literature, film, and even real-world events, offering frameworks to comprehend personal and shared experiences.
Archetypes and the Universe
Archetypes transcend psychological and cultural dimensions, extending into the physical universe. In cosmology, scientists search for simple patterns that explain complex phenomena, akin to the search for archetypes. The idea that the universe might be underpinned by a set of primordial patterns aligns with philosophical interpretations of reality as a structured entity, governed by metaphysical and mathematical truths.
“The laws of nature are but the mathematical thoughts of God.” — Euclid
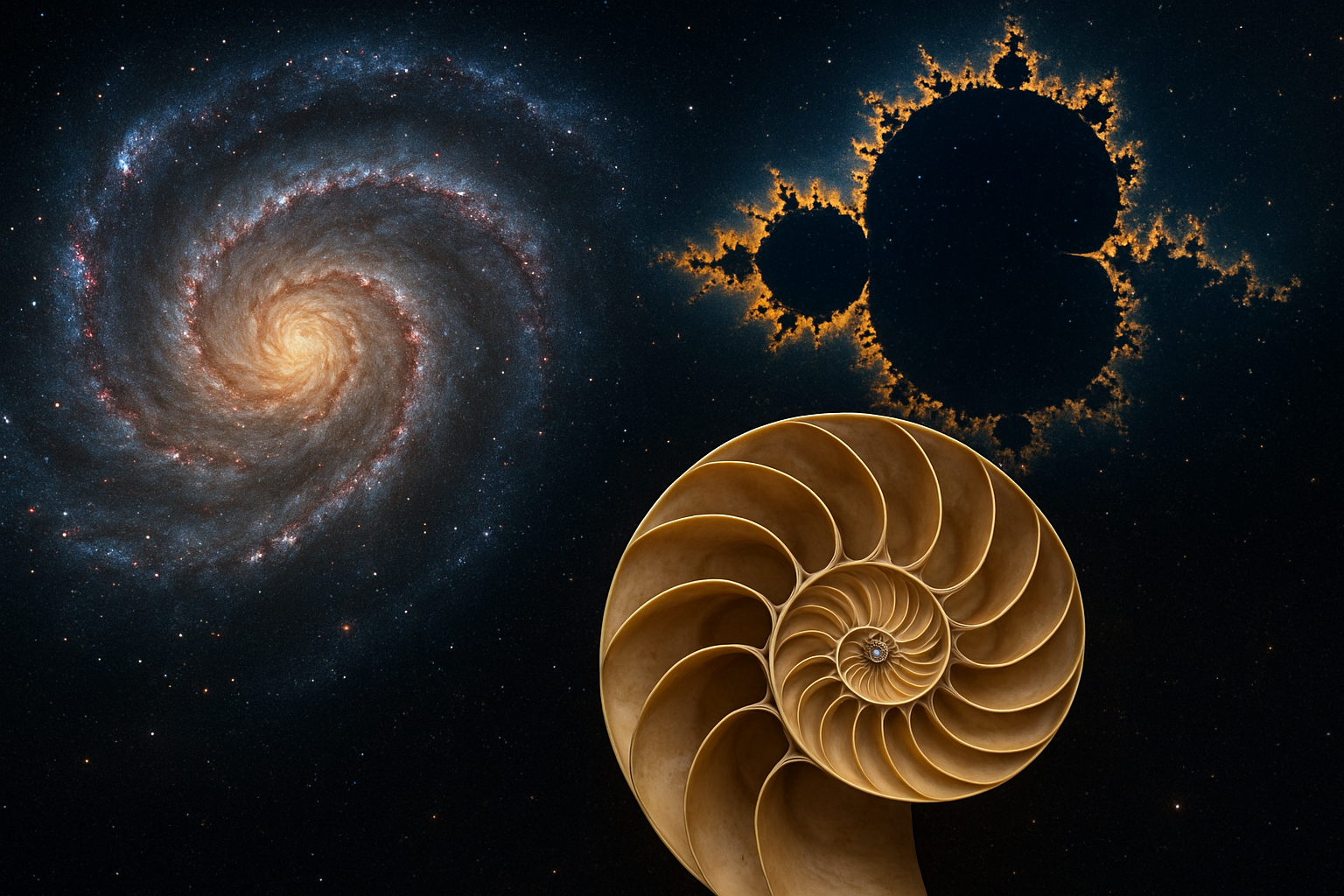
The laws of physics can be seen as the archetypal forces shaping the cosmos. Concepts like symmetry, fractals, and chaos theory suggest the presence of recurring patterns and principles. Symmetry, for instance, underlies the laws of physics, manifesting in the symmetrical properties of particles and fields. Fractals, on the other hand, represent self-similarity across scales, offering a visual and conceptual parallel to Jung’s archetypes within a universal context.
The Intersection of Archetypes in Science and Philosophy
Philosophy provides a crucial lens through which to explore archetypes as both metaphysical entities and guiding principles in scientific inquiry. The notion of epistemic archetypes implies that our pursuit of knowledge is shaped by archetypal understandings, influencing scientific revolutions and the evolution of paradigms. Thomas Kuhn’s concept of paradigm shifts in The Structure of Scientific Revolutions aligns with this perspective, reflecting the dynamic interplay between old and new archetypes in scholarly progress.
Additionally, Plato’s theory of Forms can be considered an antecedent to Jungian archetypes. Forms are perfect, immutable archetypes of objects and concepts in the world, of which the physical manifestations are merely imperfect copies.
“The theory of forms… suggests that the visible world is an imperfect, perhaps shadowy imitation of the ‘world of forms’.” — Plato
Integrating archetypal patterns into philosophical and scientific discourses allows for a holistic understanding of reality, one that acknowledges both the tangible and intangible dimensions of existence.
The Relevance of Archetypes Today
In an era where artificial intelligence and technological advancements reshape our world, archetypes remain deeply relevant. They serve as ethical and existential anchors as humanity navigates complexities of modern life. In machine learning, for example, pattern recognition mimics archetypal processes by identifying essential variables from vast datasets, drawing parallels to how humans intuitively recognize archetypes.
Furthermore, cultural and psychological archetypes provide frameworks for exploring identity and meaning in a globalized society, fostering shared understanding across diverse backgrounds. They remind us of the intrinsic interconnectedness of human experiences and the universe.
“We must let go of the life we have planned, so as to accept the one that is waiting for us.” — Joseph Campbell
In summary, the exploration of primordial patterns and archetypes presents a timeless dialogue between humanity, the cosmos, and the unknown. It invokes a sense of wonder and curiosity, inviting us to delve deeper into the essence of reality and our place within it.
For a more in-depth exploration of archetypes, the works of Joseph Campbell and Carl Jung provide valuable insights and foundational knowledge.