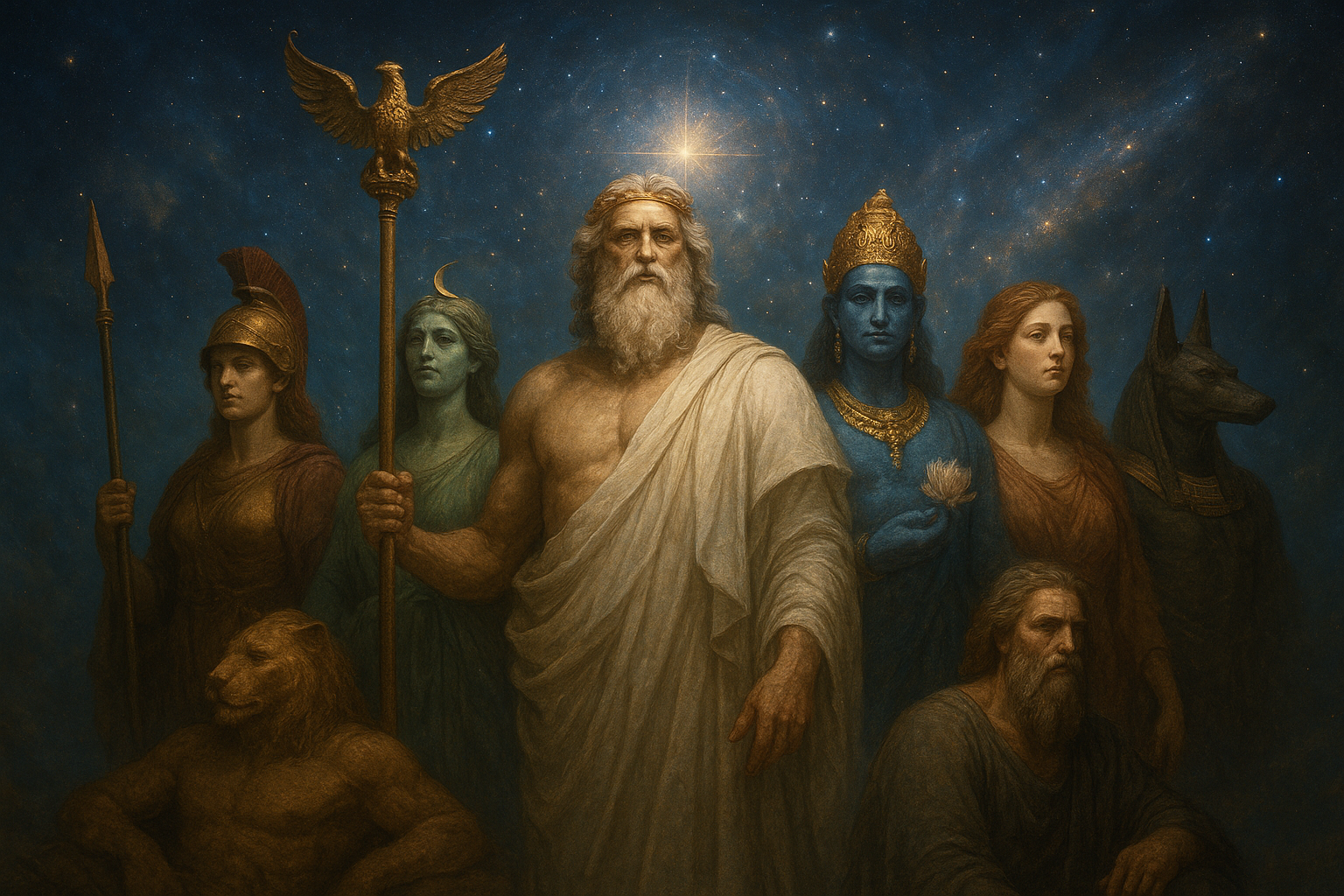
Throughout history, humans have gazed upwards, mesmerized by the stars and the vast cosmos, often attributing divine qualities to the celestial bodies. This cosmic wonder has incubated a rich tapestry of astral deities and mythologies across diverse cultures. From the winged messengers of ancient Zoroastrianism to the heavenly chariots of Vedic texts, astral deities have played a significant role in shaping human civilization.
Origins in Ancient Mythologies
- Egyptian Skylore: In ancient Egypt, the sky was personified as the goddess Nut, who arched over the earth with her star-strewn body. Nut was seen as a protector of the dead and a symbol of resurrection, with pharaohs often depicted joining her in the afterlife to become stars themselves.
- Mesopotamian Guardians: For the Babylonians, the stars were the domain of Sin, the god of the moon, who wielded great astrological influence. The god Anu was revered as the father of the gods, representing the epitome of the celestial cosmos.
Influence of the Greek and Roman Pantheon
The Greeks wove intricate tales that integrated their gods with the constellations seen in the night sky. Familiar figures such as Orion the Hunter and Andromeda were enshrined in the heavens as stars that linked human fate with celestial movements.
“The heavens declare the glory of God; and the firmament sheweth his handiwork.” — Psalm 19:1 (KJV)
This sentiment was mirrored in Roman culture, where constellations were named after heroic figures and mythological stories, echoing their origins in Greek astronomy.
Eastern Concepts and Beyond
- Chinese Celestial Bureaucracy: In ancient Chinese belief, the sky was a complex bureaucratic structure with the Jade Emperor presiding over it all. Each star and planet was seen as a celestial administrative unit with specific responsibilities influencing earthly affairs.
- Hindu Astronomy: The Vedic concept of Navagraha, the nine celestial influencers, remains vital in Hindu astrology today. These astral deities, such as Surya (the sun) and Chandra (the moon), directly impact human lives according to Hindu belief.
The Modern Cosmic Perspective
Although technological advances have shifted our understanding of celestial bodies, the mythological allure remains potent. Astral deities continue to intrigue us, serving as powerful symbols in literature, film, and art — reminders of the timeless human quest to connect the earthly with the divine.
The astral pantheon, with its countless interpretations across the annals of history, continues to enrich our collective imagination, reflecting a profound legacy of humanity’s connection with the universe.